
- by Sharon Wauer
- September 21, 2025
- Appraisal Services, Diamonds, Resources
When it comes to diamonds, the 4Cs—Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat—are the universal standard for assessing quality. Developed by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), these characteristics ensure transparency and consistency in diamond grading.
1. Cut
The cut of a diamond determines its brilliance and sparkle. A well-cut diamond reflects light beautifully, creating a dazzling effect. Graded from Excellent to Poor, the cut is a critical factor in a diamond’s overall appearance.
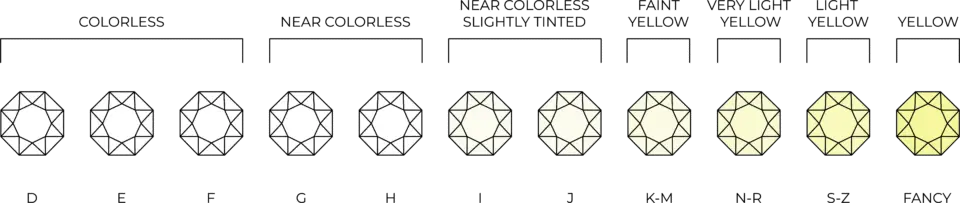
2. Color
Diamond color is graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). Colorless diamonds are the most valuable, but near-colorless options (grades G-J) offer excellent value without compromising beauty.
3. Clarity
Clarity measures the presence of inclusions (internal flaws) and blemishes (surface flaws). The GIA clarity scale ranges from Flawless (FL) to Included (I3). Most diamonds have imperfections, but many are invisible to the naked eye.

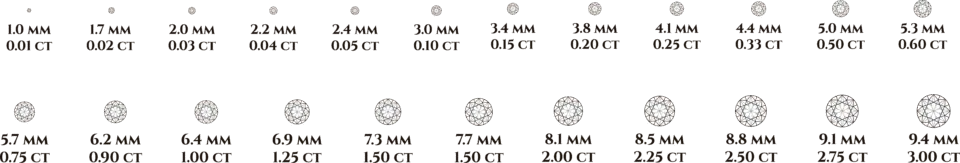
4. Carat
Carat refers to a diamond’s weight, with one carat equaling 200 milligrams. While carat weight influences size, a well-cut diamond can appear larger than its actual weight.
Tips for Finding Your Perfect Diamond
- Prioritize Cut: A high-quality cut enhances brilliance, even in smaller diamonds.
- Balance Color and Clarity: Near-colorless diamonds with slight inclusions often provide the best value.
- Consider Carat Weight: Opt for slightly below popular weights (e.g., 0.9 carats) to save without sacrificing size.
Types of Diamonds
- Natural Diamonds: Formed over billions of years, these are prized for their rarity and timeless appeal.
- Lab-Grown Diamonds: Identical in composition to natural diamonds but more affordable and eco-friendly.
Certification Matters
Always choose diamonds certified by reputable organizations like GIA or IGI to ensure quality and authenticity.

